Aerosols, tiny particles suspended in the atmosphere, play a critical but complex role in the quest to understand our planet’s climate system. They can be dust from natural sources or pollutants produced by humans, and their impact can range from altering climate patterns to affecting air quality and human health. Shedding light on these elusive components, the Dutch-engineered instrument SPEXone has been launched aboard NASA’s PACE satellite, providing unprecedented insights into the global distribution and characteristics of aerosols.
The SPEXone Mission
Launched on February 8, 2024, from Cape Canaveral, the PACE satellite, developed by NASA, aimed to study multiple factors that determine Earth’s climate. Among the instruments onboard the satellite, the SPEXone is one of the most technologically advanced for the analysis of aerosols with high accuracy. Developed through a collaboration between SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands, with support from TNO, SPEXone represents a significant advancement in atmospheric research.
Understanding Aerosols
Aerosols are minute particles or droplets suspended in the atmosphere. They originate from both natural processes, such as volcanic eruptions and sea spray, and human activities, including industrial emissions and vehicle exhaust. Depending upon their properties, some aerosols can cool or warm the planet. The cooling aerosol effects are primarily due to reflective aerosols like sulfate particles, that force the sun’s scattered light back into space. In contrast, absorbing aerosols with prevailing properties like black carbon from combustion processes trap heat and contribute to warming.
In addition to these direct climatic effects, aerosol particles also act as nuclei for the formation of clouds. Water vapor condenses into droplets over these particles, leading to their aggregation forming cloud droplets. The amount and kind of aerosols affect cloud properties and hence their reflectivity and life span, thus altering weather and climatic phenomena.
SPEXone Capabilities
SPEXone is one of the compact and sophisticated instruments designed for measuring polarization of sunlight when it interacts with Earth’s atmosphere. Data received from five different angles using SPEXone would help determine size, composition, shape, and of course, reflective or absorptive characteristics of aerosols. This multi-angle approach can separate the fine particles contributing to industrial pollution from coarser particles-these are mostly seen as desert dust or sea salt.
The measurement of DoLP and AoLP of reflected sunlight is a prominent feature of SPEXone. These measurements are crucial in detailing the type and distribution of aerosols, which are necessary for refining climate models and our understanding of the impact of aerosols on climate change.
First Light: A New Perspective on Aerosols
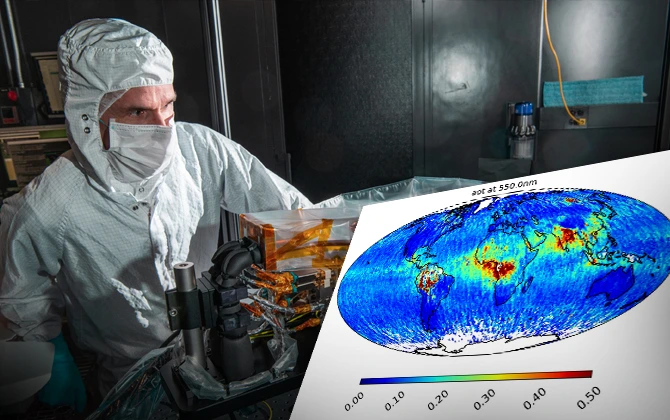
Shortly after its launch, SPEXone successfully completed its “First Light” milestone when it was able to acquire first light images that depicted Earth’s atmosphere from a new perspective. Its early observations showed that the instrument could successfully distinguish between different types of aerosols and particles of varying sizes across different regions. For example, over regions of significant industrial activities, SPEXone captured higher amounts of fine particles, whereas areas dominated by natural sources- such as deserts and oceans-even emitted coarser particles.
These first results highlight the capability of the instrument to increase our knowledge on the distribution of aerosols and their climatic impact. It will allow scientists to generate global, high-resolution aerosol maps with multi-angle polarization data that could provide clues on the contributions of both natural and anthropogenic factors to atmospheric composition.
Climate Research Implications
For climate scientists, this data is a treasure trove in reducing the uncertainties of climate models. One of the greatest unknowns that plague climate projections is aerosols, mainly due to their source diversity and their complex interactions in the atmosphere. Accurate characterization of aerosols is necessary in understanding their net effect on Earth’s energy balance.
This would allow scientists to better predict future climate scenarios by incorporating SPEXone’s high-resolution aerosol measurements into climate models. It would help to separate the cooling effects of reflective aerosols from the warming effects of absorbing ones, thus allowing for more accurate assessments of human influence on climate change.
Beyond Climate: Air Quality and Public Health
While SPEXone’s primary mission focuses on climate research, its data also holds promise for air quality monitoring and public health applications. Aerosols are a major component of air pollution, which poses significant health risks, including respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. By mapping aerosol concentrations and types globally, SPEXone can help identify pollution hotspots and track the movement of harmful particles.
This will be vital to policymakers and health officials for making targeted mitigation and protection of those most at risk from the harms of air pollution. Further, knowing how the aerosols distribute can also give rise to very early warning of events like a dust storm or wildfire smoke plume so as to make an early public advisory.
Collaboration Needed
International collaboration succeeds in advancing Earth science, as well-established by the development of SPEXone. Combining Dutch research institutions with NASA signifies how one can make excellence accomplished through multiple research institutions. It represented how various organizations merged to bring into the limelight SPEXone, developed with the collaboration of SRON and Airbus Defence and Space Netherlands and TNO, as important enough about interdisciplinary cooperation in terms of environmental challenges.
As SPEXone continues its work aboard the PACE satellite, the scientific community is eager for the tremendous body of data, which will illuminate our knowledge and understanding of the multifaceted roles aerosols play in the Earth’s climate system. What is gained there will enhance our climate models while informing policies targeted at mitigating climate change as well as ameliorating air quality.
In a world where the effects of climate change are becoming increasingly evident, tools like SPEXone provide the detailed observations necessary to inform effective action. Illuminating the hidden dynamics of aerosols, SPEXone brings us one step closer to unraveling the complexities of our planet’s atmosphere and safeguarding its future.