Introduction
Jupiter’s Great Red Spot (GRS), an antipodal storm larger than Earth, has drawn the interest of astronomers for decades. The famous feature has astonished scientists in 2024 with unexpected size changes and dynamic motions. This year’s observations, primarily by the NASA Hubble Space Telescope, have been unprecedented about what has been learned about how the Red Spot oscillates and new theories on how such changes occur. Here’s a closer look at what has been discovered and what this means.
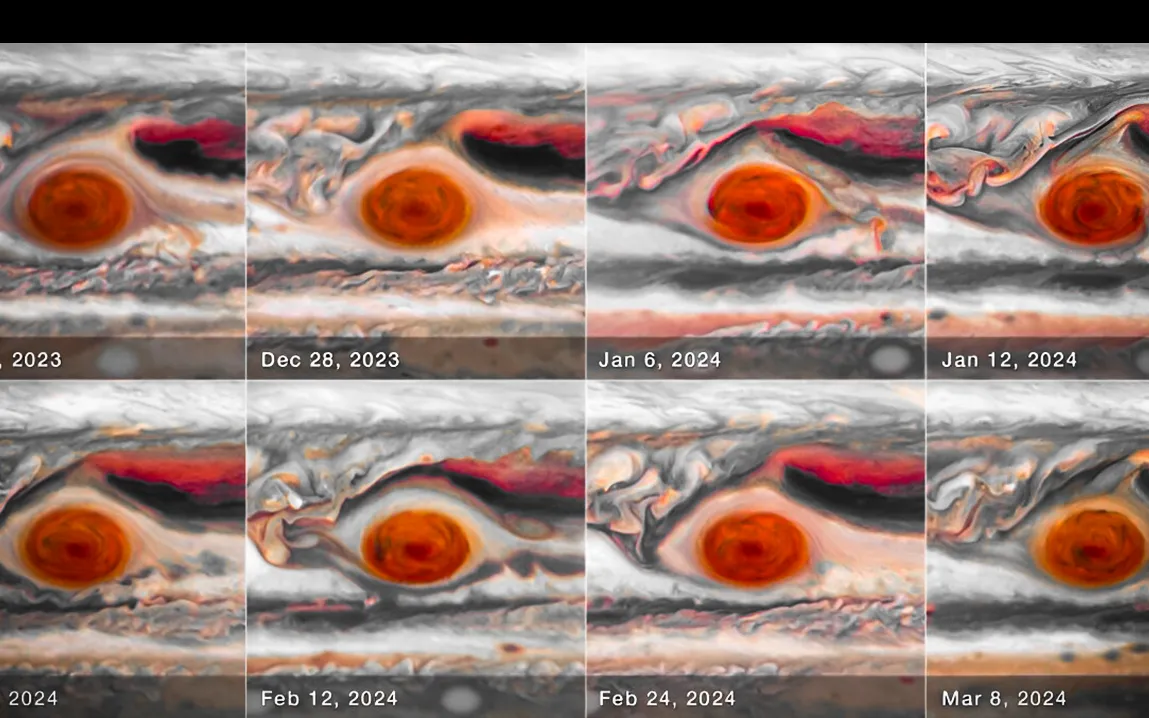
Hubble Discovers a Wiggling Storm
Between December 2023 and March 2024, NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope photographed a series of high-resolution images of the Great Red Spot. Such observations were part of a focused program designed to monitor how the storm was changing over time. For 90 days, astronomers monitored its size, shape, brightness, and motion. One of the most fascinating observations was that the GRS was “jiggling,” meaning that the enormous storm was oscillating in shape, much like a bowl of gelatin wobbling back and forth. This is the first time the behavior could be observed so vividly thanks to Hubble’s advanced imaging capabilities.
The scientists were unprepared for the fluctuations in size of the GRS. For a long time, they knew that the longitudinal motion of the storm (that is, its propagation across Jupiter’s surface) varied slightly, but the size oscillation was a discovery only now. We didn’t expect to see the size oscillate,” said planetary scientist Amy Simon of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center. New questions arise in terms of what’s happening inside Jupiter’s atmosphere since current hydrodynamic models cannot account for these changes.
A Storm in Flux: Variations in Speed and Shape
Apart from the fluctuating size, the Great Red Spot has manifested changes in both speed and shape. During the observation period, the storm alternated between acceleration and retardation. This proves that the GRS is far from being the stable and old storm that it was once reckoned to be. The other elliptical shape of the storm was observed stretching and contracting within the observation window.
The cause of these oscillations is not known precisely. Researchers do believe, however, that these fluctuations may be related to interactions with the complex systems within Jupiter’s atmosphere. Interactions could be coming from the surrounding streams of jets and even smaller vortices. These could be contributing to the dynamic behavior of the storm. Understanding these interactions could give scientists new insight into how weather similar to this might form and evolve elsewhere—on other planets, for instance, especially those exoplanets with very extreme atmospheres.
Implications for Earth and Beyond
Although the size and longevity of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot are unparalleled, the 2024 discovery has broader implications in the scientific study of planets. Studies on Jupiter’s storm systems will assist scientists in establishing models that will eventually improve the understanding of the dynamics of atmospheres on other planets, including Earth. GRS, for instance, is an exemplary natural laboratory for extreme weather patterns; large-scale anticyclones are also found on Earth.
Scientists are therefore able to use what they see happening in the GRS to nudge the entire group toward fine-tuning their theory of atmospheric turbulence and how storms develop. This is important to understanding exoplanets since so many of them are gas giants, and their atmospheres are awful and wild. As Patrick Irwin, a planetary scientist on the team, said, “The lessons we learn from the Great Red Spot could help us predict weather on planets outside our solar system.”
Continuation of the Mystery: What’s Next?
The 2024 observations are but one piece of an unbroken set of observations of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot. The NASA Outer Planet Atmospheres Legacy (OPAL) program annually monitors the outer planets and will continue to observe GRS behavior in the coming years. Meanwhile, astronomers scan the bounty of data recorded over a span of 90 days, looking for new clues about its internal structure and what forces these fluctuations in the storm.
Despite such a long time of observation, the astronomers remain astonished by the Great Red Spot. The shrinking size and changing form with the increasing and then fading speeds tell astronomers that perhaps someday this feature could dissipate or change into something entirely different. It remains one of the most iconic and intriguing features of our solar system for now.
Conclusion
A global team of astronomers made observations of Jupiter’s Great Red Spot in 2024, revealing a storm that appears to be far more dynamic and unstable than previously appreciated. Oscillating size, shape, and speed changes had astronomers raising new questions regarding what forces might drive such changes and what planetary science might see as implications for our understanding. To me, it remains a great reminder of how much mystery still awaits us in our exploration of the universe, but for astronomers, it’s just an interesting thing to continue looking at.